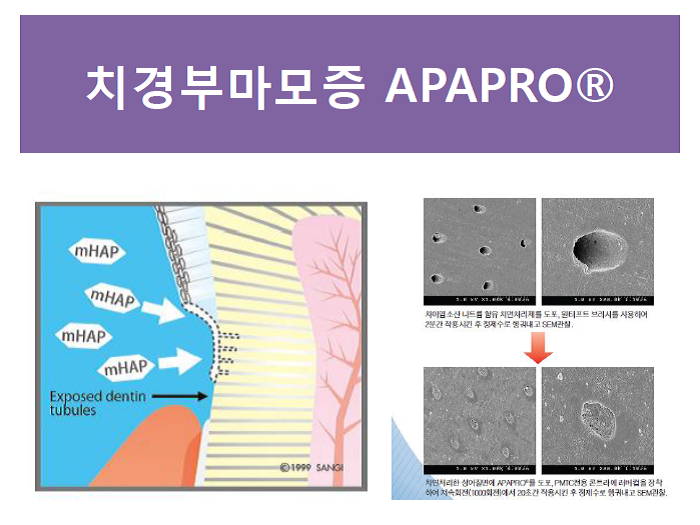
Dentinal tubule occluding capability of nano-hydroxyapatite; The in-vitro evaluation
나노 하이드록시아파타이트의 상아세관 봉쇄 능력
2018 Aug;81(8):843-854.
Authors
Serdar Baglar 1 , Umit Erdem 2 , Mustafa Dogan 2 , Mustafa Turkoz 3
Affiliations
-
1 Department of Restorative Dentistry, Faculty of Dentistry, Kirikkale University, Kirikkale, 71450, Turkey.
-
2 Scientific and Technological Research Application and Research Center, Kirikkale University, Kirikkale, 71450, Turkey.
-
3 Faculty of Engineering, Department of Electric and Electronics Engineering, Karabük University, Karabuk, 78050, Turkey.
Abstract
In this in-vitro study, the effectiveness of experimental pure nano-hydroxyapatite (nHAP) and 1%, 2%, and 3% F¯ doped nano-HAp on dentine tubule occlusion was investigated. And also, the cytotoxicity of materials used in the experiment was evaluated. Nano-HAp types were synthesized by the precipitation method. Forty dentin specimens were randomly divided into five groups of; 1-no treatment (control), 2-specimens treated with 10% pure nano-HAp and 3, 4, 5 specimens treated with 1%, 2%, and 3% F- doped 10% nano-HAp, respectively. To evaluate the effectiveness of the materials used; pH, FTIR, and scanning electron microscopy evaluations were performed before and after degredation in simulated body fluid. To determine cytotoxicity of the materials, MTT assay was performed. Statistical evaluations were performed with F and t tests. All of the nano-HAp materials used in this study built up an effective covering layer on the dentin surfaces even with plugs in tubules. It was found that this layer had also a resistance to degradation. None of the evaluated nano-HAp types were have toxicity. Fluoride doping showed a positive effect on physical and chemical stability until a critical value of 1% F- . The all evaluated nano-HAp types may be effectively used in dentin hypersensitivity treatment. The formed nano-HAp layers were seem to resistant to hydrolic deletion. The pure and 1% F- doped nano-HAp showed the highest biocompatibility thus it was assessed that pure and 1% F- doped materials may be used as an active ingredient in dentin hypersensitivity agents.
순수 나노하이드록시아파타이트와 1% 불소이온 도포 하이드록시아파타이트가 가장 높은 생체친화성을 보여 주었고 상아질지각과민에 효과적인 물질로 사용 될 수 있다.
Keywords: cytotoxicity; degredation; dentine hypersensitivity; dentine tubule occlusion; fluoride; hydroxyapatite.
[Effect of nanohydroxyapatite on surface mineralization in acid-etched dentinal tubules and adsorption of lead ions]
산처리된 상아세관들에 대한 나노하이드록시아파타이트와 납이온의 흡수로 인한 표면 광화효과
. 2020 Sep 30;40(9):1307-1312.
Authors
Jianzhen Yang 1 , Peiyan Yuan 1 , Chengxia Liu 1 , Ping Liu 1 , Huili Ning 1 , Pingping Xu 1
Affiliation
-
1 Department of Endodontics, Stomatological Hospital, Southern Medical University/Guangdong Provincial Hospital of Stomatology, Guangzhou 510280, China.
Abstract
Objective: To study the effect of nanohydroxyapatite (nHA) for promoting surface mineralization of demineralized dentin discs and adsorption of lead ions in simulated sewage water.
Methods: Sixty dentin disks were prepared from freshly extracted teeth with intact crown (including 30 premolars and 30 molars) and treated with 10% citric acid for 2 min to simulate dentinal tubules with dentin hypersensitivity. The etched dentin discs were brushed with distilled water, 0.2 g HA or 0.2 g nHA for 2 min twice a day for 7 consecutive days, after which scanning electron microscopy (SEM) was performed and calcium and phosphorus contents in the dentin discs were detected using EDS. Lead ion adsorption capacities of HA and nHA were tested by mixing 1 mL serial concentrations of HA and nHA suspensions with 50 mL lead ion solutions (1.0 mg/L). After 24 h, the residual lead ion concentration in the supernatant was measured using ICP to calculate lead ion adsorption rate and adsorption capacity of the materials.
Results: SEM showed a smooth surface and empty dentin tubules in the acid- etched dentin dics. The dentin dics treated with HA were covered with masses of particles that loosely attached to the surface, and the diameter of the dentin tubules was reduced. In nHA group, the dentin discs showed a fine and homogeneous surface clogging with a tight attachment, and the dentin tubule diameter was obviously reduced. Daily brushing with HA and nHA, especially the latter, significantly increased calcium and phosphorus contents on the surface of the dentin dics (P < 0.000). In lead ion adsorption experiment, the lead ion adsorption rate of HA decreased as its concentration increased with the highest adsorption rate of 83.01%; the adsorption rate of nHA increased with its concentration until the adsorption equilibrium was reached, and its highest adsorption rate was 98.79%. A good liner relationship was found between the adsorption ability and concentration of HA.
Conclusions: Compared with HA, nHA has a better capacity for surface mineralization of acid-etched dentin discs and also a better ability of lead ion adsorption.
하이드록시아파티이트와 나노입자 하이드록시아파타이트의 산처리된 상아질 표면의 재광화효과를 비교할 때 나노 하이드록시아파타이트가 훨씬 뛰어난 납이온 흡수력을 보여 주었다.
Keywords: adsorption; dentin hypersensitivity; lead ions; nanohydroxyapatite; surface mineralization.
J Conserv Dent
Evaluation of dentinal tubule occlusion and depth of penetration of nano-hydroxyapatite derived from chicken eggshell powder with and without addition of sodium fluoride: An in vitro study
계란 껍데기에서 추출한 나노 하이드록시아파타이트의 상아세관 봉쇄와 침투 깊이 평가: 불소와 함께 또는 불소 없이
Divya Kunam et al. J Conserv Dent. May-Jun 2016.
Authors
Divya Kunam 1 , Sujatha Manimaran 1 , Vidhya Sampath 1 , Mahalaxmi Sekar 1
Affiliation
-
1 Department of Conservative Dentistry and Endodontics, SRM Dental College, Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India.
Abstract
Aim: This in vitro study evaluated the degree of dentinal tubule occlusion and depth of penetration of nano-hydroxyapatite (nHAp) derived from chicken eggshell powder with and without the addition of 2% sodium fluoride (NaF) using scanning electron microscope (SEM) and confocal laser scanning microscope (CLSM).
Materials and methods: nHAp was synthesized and characterized using X-ray diffraction and SEM-energy dispersive spectroscopy. Dentin discs were obtained from extracted teeth, pretreated with 17% ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid for 5 min and were divided into four groups based on the experimental agents as follows: Group 1: Untreated (control), Group 2: 2% NaF, Group 3: nHAp, Group 4: Combination of nHAp and 2% NaF. The treatment protocol was carried out for 7 days, after which the specimens were viewed under SEM and CLSM.
Statistical analysis used: One-way ANOVA and Tukey's post hoc multiple comparison tests (P < 0.05).
Results: All the experimental agents occluded the dentinal tubules, but to varying degrees and depths. Specimens treated with the combination of nHAp and 2% NaF showed complete dentinal tubular occlusion and significantly greater depth of penetration than those treated with nHAp and 2% NaF alone.
Conclusion: The combination of nHAp and 2% NaF was the most effective in occluding dentinal tubules.
나노 하이드록시아파타이트와 2% NaF 조합이 상아세관 봉쇄에 가장 효과적이었다.
Keywords: Dentin hypersensitivity; desensitizing agents; eggshells; hydroxyapatite; sodium fluoride; tubule occlusion.
Randomized Controlled Trial
Oper Dent
Treatment of Dentin Hypersensitivity Using Nano-Hydroxyapatite Pastes: A Randomized Three-Month Clinical Trial
나노하이드록시아파타이트 페이스트를 이용한 상아질지각과민 처치: 3개월 임상 실험
. Jul-Aug 2016;41(4):E93-E101.
Authors
L Wang, A C Magalhães, L F Francisconi-Dos-Rios, M P Calabria, Dfg Araújo, Mar Buzalaf, Jrp Lauris, J C Pereira
Abstract
Objectives: This randomized clinical trial tested the three-month desensitizing effect of two protocols using nano-hydroxyapatite formulations compared with Pro-Argin and fluoride varnish.
Methods: Twenty-eight subjects with 137 teeth presenting dentin exposure with a minimal hypersensitivity of four on the visual analog scale (VAS) took part of this study. The subjects were randomly assigned to four groups: Desensibilize Nano-P paste (20% hydroxyapatite [HAP], potassium nitrate, and sodium fluoride [NaF]; 9000 ppm fluoride [F]); Desensibilize Nano-P associated with experimental home-care pastes (10% HA, potassium nitrate, and NaF; 900 ppm F); Pro-Relief professional paste (8% arginine with Pro-Argin technology) associated with home-care toothpaste (8% arginine, sodium monofluorophosphate, 1450 ppm F); and Duraphat professional varnish (NaF varnish, 22,600 ppm F). The professional treatments were performed in weekly appointments over three weeks. The home-care products were used continuously for three months. A VAS was used to assess the tooth sensitivity response after standardized evaporative stimulus at baseline and after one month and three months. The baseline score was deducted from the final score, and the means were analyzed using nested analysis of variance, while the comparison between times was performed by a general linear model (p<0.05).
Results: At the first month all treatments were effective, but there were no significant differences among them (p=0.94). At the third month, despite the fact that NaF varnish had the lowest effect in reducing hypersensitivity, no significant difference was found among the treatments (p=0.09). Only Pro-Relief increased its effect over time (p=0.049).
Conclusions: Nano-hydroxyapatite formulations (with or without home->care product association) were as effective as the other treatments in reducing dentin hypersensitivity over three months.
나노 하이드록시아파타이트의 상아질 지각과민의 감소효과(3개월 처치)는 다른 치료들(바니쉬등) 만큼 효과적이다.
Meta-Analysis, J Dent
Clinical efficacy of nano-hydroxyapatite in dentin hypersensitivity: A systematic review and meta-analysis
나노 하이드록시아파타이트의 상아질 지각과민 처치의 임상적 효과성
: 체계적 리뷰 및 메타분석
Cristiane de Melo Alencar et al. J Dent. 2019 Mar.
Authors
Cristiane de Melo Alencar 1 , Brennda Lucy Freitas de Paula 1 , Mariangela Ivette Guanipa Ortiz 1 , Marcela Baraúna Magno 2 , Cecy Martins Silva 3 , Lucianne Cople Maia 2
Affiliations
-
1 School of Dentistry, Federal University of Para, Belém, PA, Brazil.
-
2 School of Dentistry, Federal University of Rio de Janeiro, Rio de Janeiro, RJ, Brazil.
-
3 School of Dentistry, Federal University of Para, Belém, PA, Brazil. Electronic address: cecymsilva@gmail.com.
Abstract
Objectives: To evaluate the desensitizing effect of nano-hydroxyapatite (n-HAP) on dentine hypersensitivity (DH).
Sources: Seven electronic databases were searched on April 27, 2018.
Study selection: Randomized clinical trials (RCTs) were included based on the PICO strategy: Participants - Humans with DH; Intervention - n-HAP-containing desensitizing; Comparison -n-HAP-free treatments or placebo/negative control; and Outcomes - relief of DH. The risk of bias was classified by the Cochrane guidelines. Five meta-analyses were performed to evaluate the efficacy of n-HAP with regard to pain assessment stimuli (primary outcome); comparison of n-HAP with other treatments or placebo/negative control, and effectiveness of at-home and in-office n-HAP use (secondary outcomes). The quality of the evidence was evaluated using the GRADE.
Data: Six RCTs with 4 weeks of follow-up were included in the meta-analysis. For the primary outcome, n-HAP showed a better desensitizing effect for evaporative stimuli (SMD -1.09 [-1.24, -0.94], p < 0.00001) and tactile stimuli (SMD -0.93 [-1.42, -0.43]) than other treatments (p = 0.0002). However, there was no difference between n-HAP and other treatments for the cold stimuli (SMD -0.17 [-0.81, 0.48], p = 0.61). In an overall analysis, n-HAP-containing treatment showing the most significant desensitizing effect (SMD -0.93 [-1.19, -0.68], p < 0.00001) with a high quality of evidence for pooled results. In the secondary outcomes, n-HAP showed the best effect in the overall analysis (p < 0.05) with moderate quality evidence.
Conclusions: The n-HAP-containing treatment showed better clinical performance than other treatments for DH relief. However, long-term follow-up RCTs are required in the future before definitive recommendations can be made.
나노 하이드록시아파타이트 처치는 다른 상아질지각과민 처치보다 뛰어난 임상결과를 보여 주었다.
Clinical significance: Dentin hypersensitivity is a common global condition and its multifactorial etiology has led to the development of several treatments. The n-HAP-containing treatment showed greater DH relief when compared to other desensitizing agents, placebo or negative control.
Keywords: Clinical trials; Dentin hypersensitivity; Desensitizing agents; Meta-analysis.
Randomized Controlled Trial Clin Oral Investig
Reducing dentine hypersensitivity with nano-hydroxyapatite toothpaste: a double-blind randomized controlled trial
상아질지각과민 감소 와 나노 하이드록시아파타이트 치약
M Vano et al. Clin Oral Investig. 2018 Jan.
Authors
M Vano 1 , G Derchi 1 2 , A Barone 3 , R Pinna 4 , P Usai 5 , U Covani 1 2
Affiliations
-
1 Dept of Surgical Pathology, Medicine, Molecular and Critical Area, University of Pisa, Pisa, Italy.
-
2 Tuscan Stomatologic Institute, Viareggio, Italy.
-
3 Dept of Oral Surgery, University of Geneva, Genève, Switzerland.
-
4 Dept of Biomedical Sciences, University of Sassari, Viale San Pietro 43/C, 07100, Sassari (SS), Italy.
-
5 Dept of Biomedical Sciences, University of Sassari, Viale San Pietro 43/C, 07100, Sassari (SS), Italy. rpinna@uniss.it.
Abstract
Objectives: The present randomized double-blind clinical trial aimed to compare the efficacy in reducing dentin hypersensitivity of a dentifrice formulation containing nano-hydroxyapatite with a fluoride dentifrice and a placebo.
Methods and materials: One hundred and five subjects were recruited to participate in the study. A computer-generated random table with blocking to one of the three study treatments was used in order to have 35 subjects per group: (1) nano-hydroxyapatite 2% gel toothpaste fluoride free; (2) fluoride gel toothpaste; (3) placebo. Groups 1, 2, and 3 were instructed to treat their teeth for 10 min twice a day with the provided toothpaste gel. The participant's dentin hypersensitivity was evaluated at baseline and after 2 and 4 weeks using airblast and tactile tests. In addition, a subjective evaluation using a visual analogue scale was used.
Results: Significant lower values of cold air sensitivity and tactile sensitivity (p < 0.05) were found for the test group at 2 weeks and 4 weeks. In addition, statistically significant (p < 0.05) lower values of sensitivity were reported for group 1 compared to those for groups 2 and 3 at 2 and 4 weeks, respectively. The VAS scores were significantly lower (p < 0.05) in the test group at 2 and 4 weeks compared to those at baseline and in the control groups.
Conclusion: The application of nano-hydroxyapatite in gel toothpaste fluoride free is an effective desensitizing agent providing relief from symptoms after 2 and 4 weeks.
무불소 나노 항이드록시아파타이트 페이스트의 적용(2주 와 4주)는 지각과민증상을 완화하는 효과적인 방법이다.
Keywords: Dentine hypersensitivity; Desensitizing agents; Fluoride; Nano-hydroxyapatite.

자연치아 살리기
아파프로 나노케어
아파프로® 나노케어™
www.apadent.kr
'충치예방(치아재광화)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 밀킨, 균을 보다! 스마트폰으로 보는 신개념 위상차현미경 (0) | 2020.11.25 |
|---|---|
| 치아미백 후 시린이엔 아파프로~ (0) | 2020.11.25 |
| 오스코 최소침습 예방 관련 제품들 (0) | 2020.11.23 |
| 우리가 알아야 할 치면 손상 위험들: 플라그, 치면 스크래치, 탈회, 치근면노출, 치면착색 (0) | 2020.11.18 |
| 아파프로 나노케어 예방 세미나 (0) | 2020.11.11 |



