치과레이저치료시 나노 하이드록시아파타이트를 함께 사용하면 시린이 치료에 도움이 됩니다.
ScientificWorldJournal. 2014; 2014: 798732.
Published online 2014 Oct 20. doi: 10.1155/2014/798732
PMCID: PMC4217242
PMID: 25386616
The Effects of CO2 Laser with or without Nanohydroxyapatite Paste in the Occlusion of Dentinal Tubules
Mohammed Abbood Al-maliky, 1 , * Ali Shukur Mahmood, 2 Tamara Sardar Al-karadaghi, 2 Christoph Kurzmann, 1 Markus Laky, 3 Alexander Franz, 4 and Andreas Moritz 1 , 3
전문 링크 https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4217242/
The aim of this study was to evaluate a new treatment modality for the occlusion of dentinal tubules (DTs) via the combination of 10.6 µm carbon dioxide (CO2) laser and nanoparticle hydroxyapatite paste (n-HAp). Forty-six sound human molars were used in the current experiment. Ten of the molars were used to assess the temperature elevation during lasing. Thirty were evaluated for dentinal permeability test, subdivided into 3 groups: the control group (C), laser only (L−), and laser plus n-HAp (L+). Six samples, two per group, were used for surface and cross section morphology, evaluated through scanning electron microscope (SEM). The temperature measurement results showed that the maximum temperature increase was 3.2°C. Morphologically groups (L−) and (L+) presented narrower DTs, and almost a complete occlusion of the dentinal tubules for group (L+) was found. The Kruskal-Wallis nonparametric test for permeability test data showed statistical differences between the groups (P < 0.05). For intergroup comparison all groups were statistically different from each other, with group (L+) showing significant less dye penetration than the control group. We concluded that CO2 laser in moderate power density combined with n-HAp seems to be a good treatment modality for reducing the permeability of dentin.
J Clin Exp Dent. 2017 Dec; 9(12): e1390–e1396.
Published online 2017 Dec 1. doi: 10.4317/jced.54044
PMCID: PMC5794115
PMID: 29410753
The effects of fractional CO2 laser, Nano-hydroxyapatite and MI paste on mechanical properties of bovine enamel after bleaching
Horieh Moosavi1 and Narjes Hakimi2
Background
This study investigated the effect of post bleaching treatments to the change of enamel elastic modulus and microhardness after dental bleaching in- vitro.
Material and Methods
Fifty bovine incisor slab were randomly assigned into five groups (n=10). The samples were bleached for three times; 20 minutes each time, by 40% hydrogen peroxide. Next it was applied fractional CO2 laser for two minutes, Nano- hydroxy apatite (N-HA) and MI-paste for 7 days and 2 minutes per day. The sound enamel and bleached teeth without post treatment remained as control groups. The elastic modulus and microhardness were measured at three times; 24 hours, 1 and 2 months. Data were statistically analyzed by two-way analysis of variance with 95% confidence level.
Results
Different methods of enamel treatment caused a significant increase in elastic modulus compared to bleached group (P<0.05). Modulus was significantly increased in 1 and 2 months (P<0/001: bleach, P= 0/015: laser, P= 0/008: NHA, P=0/010: MI paste) but there were no significantly difference between 1 and 2 months (P>0.05). There was any significance difference for hardness among treated and control groups, but hardness increased significantly by increasing storage time (P<0.05).
Conclusions
The use of the protective tested agents can be useful in clinical practice to reduce negative changes of enamel surface after whitening procedures.
Key words:Bleaching enamel, CO2 laser, MI pastes, Nano-hydroxy apatite, Microhardness, Elastic modulus.
Volume 129, September 2020, 106225
The effects on dentin tubules of two desensitising agents in combination with Nd:YAG laser: An in vitro analysis (CLSM and SEM)
Yesim Sesen Uslua,⁎ , Nazmiye Donmezb a Istanbul Okan University, Faculty of Dentistry, Department of Restorative Dentistry, Istanbul, Turkey b Bezmialem Vakif University, Faculty of Dentistry, Department of Restorative Dentistry, Istanbul, Turkey
Objectives: The aim of this study was to assess in vitro the effects of two desensitising agents containing calcium phosphate and nano-hydroxyapatite, applied alone or with Nd:YAG laser, on dentin tubule occlusion, and to determine the penetration depth. Methods: 75 extracted human 3rd molar teeth were used. The effects of desensitising treatments and erosion resistance were evaluated on dentin tubule occlusion via SEM and the dentin tubule penetration depth via CLSM. Two desensitising agents—Teethmate (TMD), (Kuraray, Japan) and Professional Oral Care Nano-hydroxyapatite (Nhap) Desensitiser (Miromed Group SA, Italy)—were used. Study groups were designated as Group 1(Control), Group 2(TMD), Group 3(TMD+Nd:YAG), Group 4(Nhap) and Group 5(Nhap+Nd:YAG) and were assigned 10 dentin discs per group. After treatment with desensitising agents and laser, dentin discs were exposed to artificial saliva for one night in samples prepared to be without erosion and a sample prepared as with erosion was exposed 3 times per day for 5 days to 0.3% citric acid cycles. The Image J programme was used to scale the images of SEM analyses. The agents were mixed with 0.1% Rhodamine B for testing penetration depth and samples were analysed with CLSM after applying with and without laser. The obtained images were evaluated using the Zeiss ZEN Lite, Zeiss Microscopy programme (Carl Zeiss, Germany). Data were analysed with MannWhitney U and Kruskal Wallis tests (p < 0.05). Results: Statistically significant differences from the control group were found in all treatment groups. The TMD +Nd:YAG group had the lowest number of open tubules before and after erosion and the highest penetration depth. The Nd: YAG laser markedly increased the efficiency of the desensitising agents.
Journal of Fundamental and Clinical Research https://jfcr.journals.ekb.eg/ ISSN 2735-023X Vol. 1, No. 2, 53-68, December 2021
Effect of Diode Laser Treatment and Nano-Desensitizing Agent on Degree of Tubular Occlusion "In Vitro Study"
Salma Raafat1 , Ola Fahmy2 , Hussein Gomaa3 , Mohamed Abd El-Hamid4 , Passant EL-Asaly5
ABSTRACT
Background: Dentin Hypersensitivity is a common dental problem affecting a huge section of every population that doesn’t have a permanent treatment yet. Aim: The purpose of this study is to compare the effect of Diode laser (940nm) and Nano-desensitizing agent on the degree of tubular occlusion compared to the conventional fluoride varnish for the treatment of dentin hypersensitivity. Materials and methods: Twenty dentin specimens were prepared from extracted human premolars. Dentin specimens will be randomly allocated in 4 groups (n=5) according to desensitizing agent used: D1 (Diode Laser (940nm), D2 (Nano-hydroxyapatite), D3 (Diode Laser + Nano-hydroxyapatite) and D4 (Fluoride). The specimens will be treated with EDTA for 2 mins to open dentinal tubules simulating Dentin Hypersensitivity. Each specimen will be evaluated at 3 different times: T0 (before material application), T1 (after material application) and T2 (after acid attack) using Environmental Scanning Electron Microscope and Image Analysis software to detect degree of occlusion of dentinal tubules. Results: Group D3 showed statistically significant tubular occlusion percentage compared to the other groups except group D1. After acid attack group D3 were the only group that showed non-statistically significant decrease in tubular occlusion percentage denoting the best resistance to acid attack, while other groups were drastically affected by the acid attack. Conclusion: Combining DL (940nm) and Nano-hydroxyapatite could be a successful treatment option for Dentin Hypersensitivity, due to its high degree of tubular occlusion effect and sustainability in the acidic environment. Keywords: Dentin Hypersensitivity, Tooth Sensitivity, Diode Lasers
18 February 2014
Does ozone enhance the remineralizing potential of nanohydroxyapatite on artificially demineralized enamel? A laser induced fluorescence study
Samuelraj Srinivasan, Vijendra Prabhu, Subhash Chandra, Shalini Koshy, Shashidhar Acharya, Krishna Kishore Mahato
Abstract
The present era of minimal invasive dentistry emphasizes the early detection and remineralization of initial enamel caries. Ozone has been shown to reverse the initial demineralization before the integrity of the enamel surface is lost. Nano-hydroxyapatite is a proven remineralizing agent for early enamel caries. In the present study, the effect of ozone in enhancing the remineralizing potential of nano-hydroxyapatite on artificially demineralized enamel was investigated using laser induced fluorescence. Thirty five sound human premolars were collected from healthy subjects undergoing orthodontic treatment. Fluorescence was recorded by exciting the mesial surfaces using 325 nm He-Cd laser with 2 mW power. Tooth specimens were subjected to demineralization to create initial enamel caries. Following which the specimens were divided into three groups, i.e ozone (ozonated water for 2 min), without ozone and artificial saliva. Remineralization regimen was followed for 3 weeks. The fluorescence spectra of the specimens were recorded from all the three experimental groups at baseline, after demineralization and remineralization. The average spectrum for each experimental group was used for statistical analysis. Fluorescence intensities of Ozone treated specimens following remineralization were higher than that of artificial saliva, and this difference was found to be statistically significant (P<0.0001). In a nutshell, ozone enhanced the remineralizing potential of nanohydroxyapatite, and laser induced fluorescence was found to be effective in assessing the surface mineral changes in enamel. Ozone can be considered an effective agent in reversing the initial enamel caries there by preventing the tooth from entering into the repetitive restorative cycle.
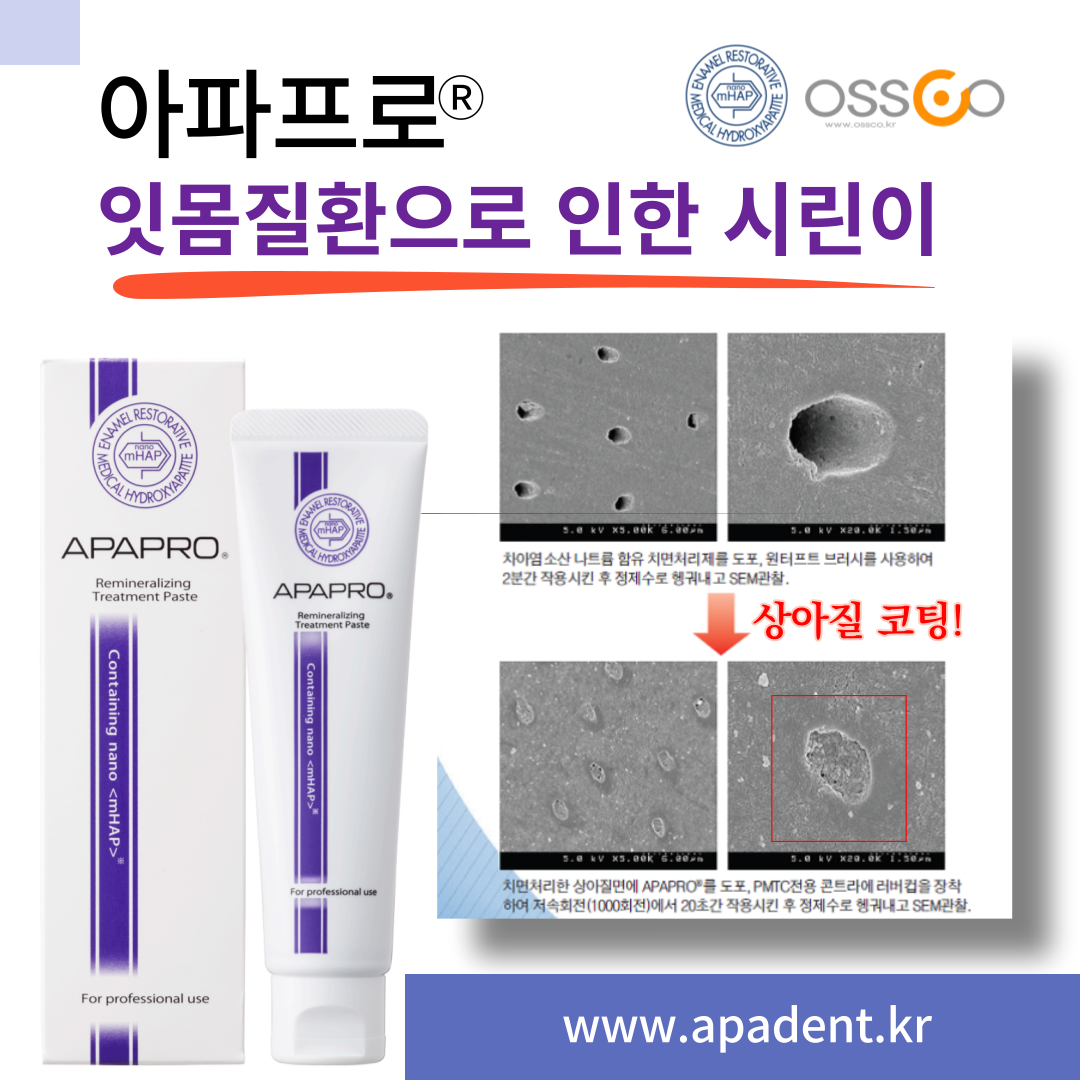

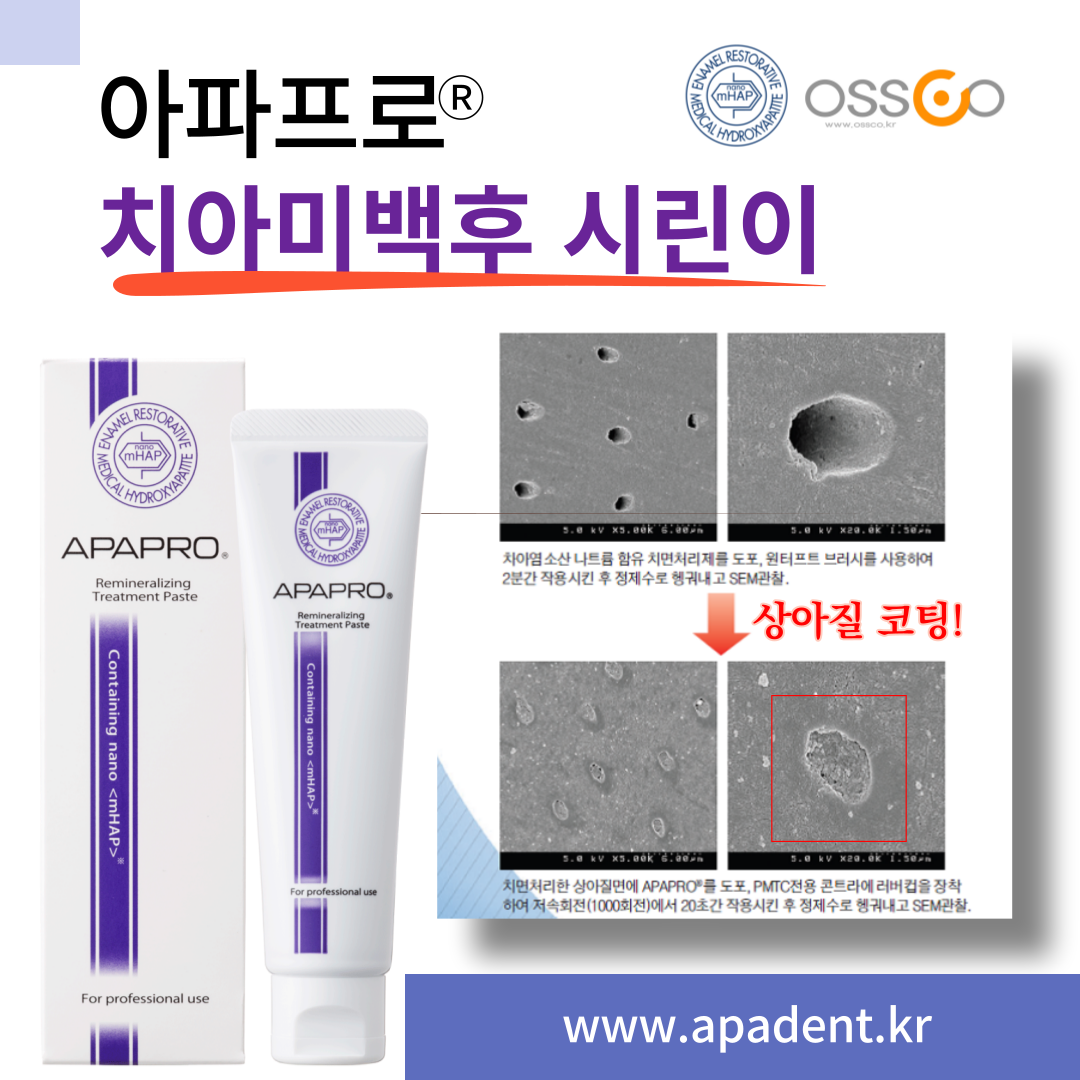


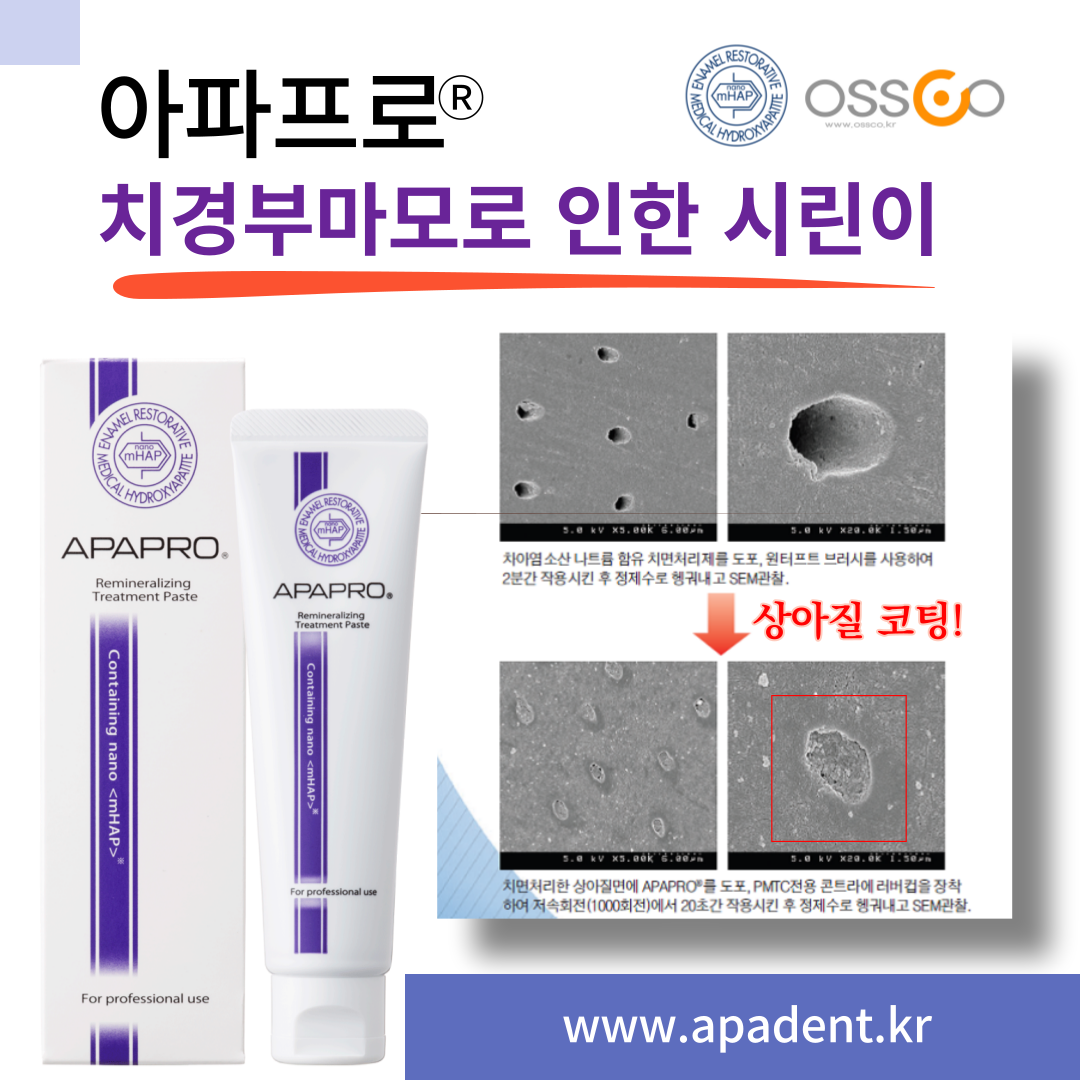
자연치아 아끼기 아파프로 나노케어
아파프로® 나노케어™
www.apadent.kr
'충치예방(치아재광화)' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 요양병원 노인구강관리~ (0) | 2022.02.18 |
|---|---|
| 요양병원, 장애인복지센타, 중환자실의 구강관리~ (0) | 2022.02.17 |
| 불소와 나노 하이드록시아파타이트의 관계 (0) | 2022.02.14 |
| 치아에 생긴 하얀 점과 얼룩, 탈회! 충치의 시작입니다. (0) | 2022.01.25 |
| 다양한 원인의 시린이! 아파프로로 관리하세요~ (0) | 2022.01.14 |



